分子量:
110.11
规格性状
规格:100 mg× 5
性状: 本产品是黄色~黄褐色固体粉末
纯度:90.0%以上
保存条件:避光冷藏;操作时注意防止吸湿
产品概述
最近的研究发现,过硫化物(Persulfide)和多硫化物(Polysulfide)等硫烷硫(Sulfane Sulfur)是生物体内的一种新型信号分子。这一类活性硫烷硫分子可以通过硫化氢释放和储存,并且与蛋白质的硫醇(Thiol)为目标的一系列信号传递(如蛋白质的巯基化等)密切相关,因此受到了广泛关注。不仅如此,过硫化物和多硫化物的还原性甚至高于半胱氨酸(Cysteine)和谷胱甘肽(Glutathione)等生物体内常见的具有还原性的物质,对维持体内的氧化还原平衡也非常重要。
Sodium polysulfide (Na2Sn)是诸多硫烷硫供体中结构最简单的一种,它在水溶液中可以随着pH的变化生成拥有多种结构的多硫化氢(Hydrogen Polysulfide, H2Sn, n≥2)。本产品是专门用于研究过硫化物、多硫化物等活性硫烷硫分子在生物体内相关通路中作用的试剂。
生物体内存在含硫烷硫分子的种类
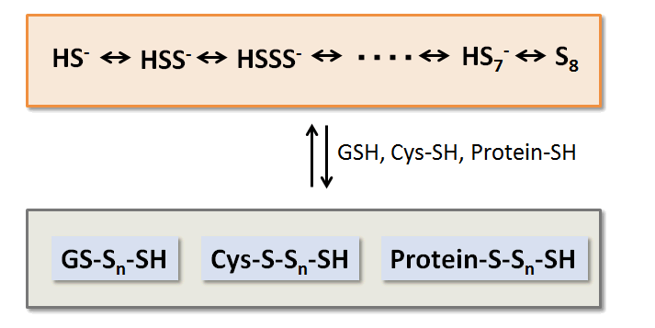
※生物体内含有硫烷硫的分子种类会随氧化还原而发生变化。
Sodium polysulfide的构造
| 供体 | Sodium disulfide(Na2S) | Sodium trisukfide(Na2S3) | Sodium tetrasulfide(Na2S4) |
| 构造 | Na+-S-S–Na+ | Na+-S-S-S-Na+ | Na+-S-S-S–Na+ |
| PKa1 | 5 | 4.2 | 3.8 |
| pKa2 | 9.7 | 7.5 | 6.3 |
| 货号 | SB02 | SB03 | SB04 |
※pKa值请参考下面文献:
J. Gun et al., “Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometric Analysis of Aqueous Polysulfide Solutions”, Microchim. Acta, 2004, 146, 229
参考文献
1) Y. Kimura, Y. Mikami, K. Osumi, M. Tsugane, J. Oka, and H. Kimura, “Polysulfides are possible H2S-derived signaling molecules in rat brain”, FASEB J., 2013, 27, 2451.
2) S. Koike, Y. Ogasawara, N. Shibuya, H. Kimura, and K. Ishii, “Polysulfide exerts a protective effect against cytotoxicity caused by t-buthylhydroperoxide through Nrf2 signaling in neuroblastoma cells”, FEBS Lett., 2013, 587, 3548.
3) E. R. DeLeon, Y. Gao, E. Huang, M. Arif, N. Arora, A. Divietro, S. Patel, and K. R. Olson , “A case of mistaken identity: are reactive oxygen species actually reactive sulfide species?”, American Journal of Physiology: Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology ., 2015, 310, (7), 549.
4) D. Delgermuruna, S. Yamaguchia, O. Ichiib, Y. Konb, S. Itoa, and K. Otsuguroa, “Hydrogen sulfide activates TRPA1 and releases 5-HT from epithelioid cells of the chicken thoracic aorta”, Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C: Toxicology & Pharmacology., 2016, 187, 43 .
5) S. Koikea, T. Kayamaa, S. Yamamotoa, D. Kominea, R. Tanakaa, S. Nishimotoa, T. Suzukia, A. Kishidab, and Y. Ogasawaraa, “Polysulfides protect SH-SY5Y cells from methylglyoxal-induced toxicity by suppressing protein carbonylation: A possible physiological scavenger for carbonyl stress in the brain”, NeuroToxicology., 2016,55, 13 .
