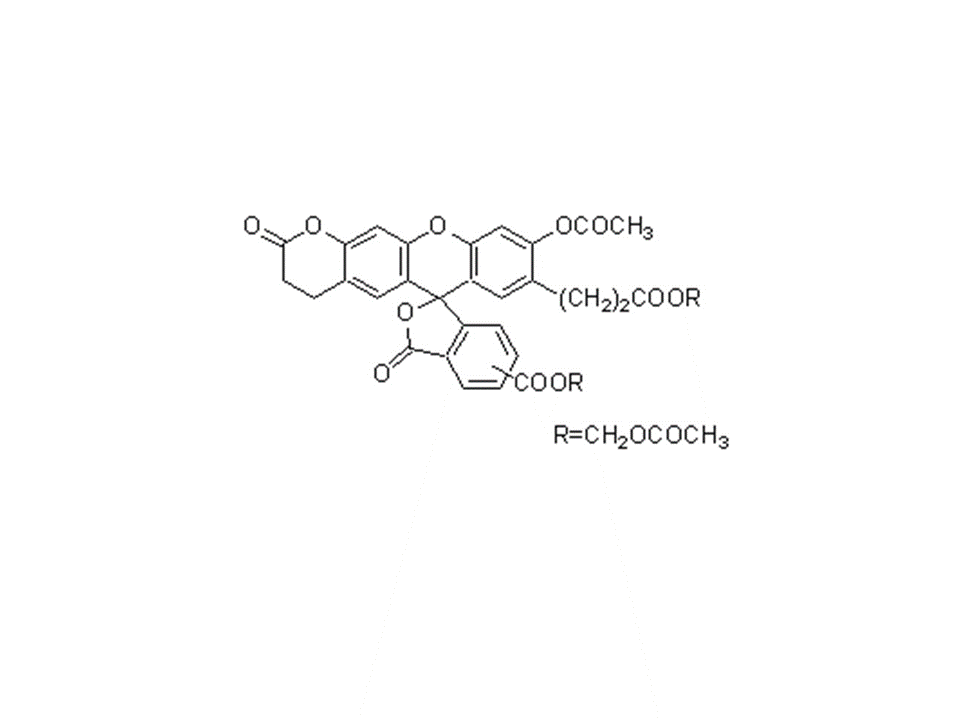
C35H28O15
688.59
特点:
● 水溶性好,可进入细胞膜
● 荧光强度高

活动进行中
订购满5000元,200元礼品等你拿
凑单关联产品TOP5
NO.1. Annexin V, FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit 细胞凋亡检测
NO.2. Cell Counting Kit-8 细胞增殖毒性检测
NO.3. Cytotoxicity LDH Assay Kit-WST 乳酸脱氢酶(LDH)检测
NO.4. Cell Viability Assay Kit 细胞增殖/毒性检测
NO.5. Fluo 4-AM special packaging 细胞内钙离子检测
规格性状
规格
特性:该产物为浅橙色至浅橙色棕色粉末或固体,可溶于DMSO和乙腈。
纯度(HPLC):90%以上
荧光光谱:试验成功
NMR光谱:试验成功
产品概述
BCECF被广泛地用于细胞内pH的测定。Tsien博士和其他人通过加入2个额外的羧化物基团改进了这种羧基荧光素。加入的两个羧基使得它能更好地被固定在细胞内。BCECF具有很好的水溶性,是因为它在中性pH时带有4-5个负电荷。但是BCECF却很难穿过细胞膜进入到细胞内。它的pKa值为6.97,高于其它的羧基荧光素。BCECF在激发光谱439nm处有等吸收点,因此它能和Fura 2一样可用比率法测定。505nm和439nm通常是非常有用的用于比率测量的波长,一般会将490nm和450nm的滤光片加在激发光源的前面。而530nm的滤光片则是用来查看它的荧光信号的。这里要注意的是激发光谱与吸收光谱有一些细微的区别。BCECF-AM是乙酰甲酯化的BCECF。它能够轻易地进入到细胞内。就和其他的乙酰甲酯类一样,BCECF-AM只需要通过孵育就能进入细胞。BCECF-AM对潮湿非常敏感,所以要小心保存。如果DMSO储存液的颜色从浅黄色变为深橙色就代表了AM的分解。所以通过对颜色变化的观测,能判断AM酯的水解情况。
产品特性
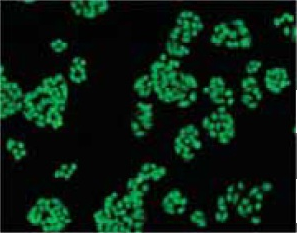
BCECF-AM是一种对细胞内pH敏感的新型荧光探针,分别用490nm和440nm波长激发BCECF所得到的发射荧光之比与pH有很好的线性关系。BCECF-AM是乙酰甲酯化的BCECF,BCECF-AM是一种可以穿透细胞膜的荧光染料,BCECF-AM没有荧光,进入细胞后被细胞内的酯酶水解成BCECF,从而被留在细胞内。BCECF在适当的pH值情况下可以被激发形成绿色荧光。BCECF-AM不仅被广泛用于哺乳动物细胞的研究,也有报道用于动物组织、植物细胞、细菌和酵母等的细胞内pH水平检测。在有细胞内pH变化的细胞毒性、细胞凋亡、细胞粘附、药物抵抗、细胞趋化等过程中BCECF AM被广泛应用。BCECF-AM(pH荧光探针)需用无水DMSO(anhydrous DMSO)配制。

操作说明
试剂 (溶解方法):
1.45 mM的BCECF-AM/DMSO溶液(将1 mg 的BCECF-AM溶于1mlDMSO)HEPES缓冲液(20mM HEPES,153mM NaCl,5mM KCl,5mM glucose,pH7.4)
操作:
1.用HEPES制备细胞悬液,细胞浓度为4×107个/ml。
2.将1.45 mM的BCECF-AM/DMSO溶液加入细胞悬液中 (细胞悬液的1/300体积),BCECF-AM终浓度为3mM。
3.37℃培养30min。
4.用HEPES缓冲液清洗细胞3次,制成3×106个/ml的细胞悬液。
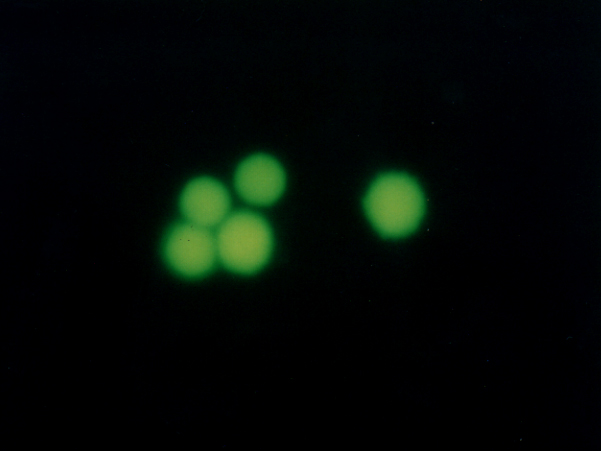
5.使用荧光显微镜或带有图像分析系统的激光共聚焦显微镜检测细胞的荧光强度。
*标记的条件因细胞种类而异,在每次实验前,请先确定最佳条件。以上方法仅供参考。
文献
1.R.A.Steinhardt, et al.,Development of K+-conductance and Membrane Potentials in Unfertilized Sea Urchin Eggs After Exposure to NH4OH. Nature.1973;241:400-401.
2.T.J.Rink, et al.,Cytoplasmic pH and Free Mg2+ in Lymphocytes.J Cell Biol.1982;95:189-196.
3.A.M.Paradiso,et al.,Na+ -H+ Exchange in Gastric Glands as Measured with a Cytoplasmic-trapped, Fluorescent pH Indicator. PNAS.1984;81:7436-7440.
4.S.Grinstein,et al.,Phorbol Ester-induces Changes of Cytoplasmic pH in Neutrophils:Role of Exocytosis in Na+ – H+ Exchange.Am J Physiol.1985;248:C379-C386.
5.G.B.Zavoico, et al.,Regulation of intracellular pH in human platelets.Effects of thrombin,A23187,and ionomycin and evidence for activation of Na+/H+ exchange and its inhibition by amiloride analogs.J Biol Chem.1986;261:13160-13167.
6.G.R.Bright,et al.,Fluorescence Ratio Imaging Microscopy: Temporal and Spatial Measurements of Cytoplasmic pH.J Cell Biol.1987;104:1019-1033.
7.C.Aalkjaer,et al.,Intracellular pH Regulation in Resting and Contracting Segments of Rat Mesenteric Resistance Vessels. J Physiol.1988;402:391-410.
8.K.Tsujimoto,et al.,Intracellular pH of Halobacteria Can Be Determined by the Fluorescent Dye 2 E 7 Ebis(carboxyethyl)-5(6)-carboxyfluorescein.Biochem Biophys Res Commun.1988;155:123-129.
9.M.A.Kolber,et al.,Measurament of Cytotoxicity by Target Cell Release and Retention of the Fluorescent Dye Bis-carboxyethylcarboxyfluorescein(BCECF).J Immunol Methods.1988;108:255-264.
10.H.Harada,et al.,cAMP Activates Cl-/HCO3 – Exchange for Regulation of Intracellular pH in Renal Epithelial Cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991;1092:404-407.11.C.C. Freudenrich, et al.,Intracellular pH Modulates Cytosolic Free Magnesium in Cultured Chicken Heart Cells.Am J Physiol.1992;262:C1024-C1030.
12.K.Khodakhah,et al.,Functional Heterogeneity of Calcium Release by Inositol Triphosphate in Single Purkinje Neurones, Cultured Cerebellar Astorocytes, and Peripheral Tissues. PNAS. 1993;90:4976-4980.
13.G.Boyarsky,et al.,Superiority of in vitro Over in vivo Calibrations of BCECF in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. FASEB J.1996;10:1205-1212.
14.S.A. Weston,et al., New Fluorescent Dyes for Lymphocyte Migration Studies Analysis by Flow Cytometry and Fluorescent Microscopy.J Immunol Methods.1990;133:87-97.
15.L.S.De Clerck,et al.,Use of Fluorescent Dyes in the Determination of Adherence of Human Leucocytes to Endothelial Cells and the Effects of Fluorochromes on Cellular Function.J Immunol Methods.1994;172:115-124.
